Prerequisite
- OS: ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is a container orchestration tool developed by Google. Kubernetes is a platform tool to manage containerized workloads and services.
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open-source platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
-- Kubernetes https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/what-is-kubernetes/
Official Interactive tutorial
If you don't want to install minikube locally, you can also try the official kubernetes interactive tutorial.
Minikube
But we don't use the tutorial. We will use Minikube to run Kubernetes locally. But what is minikube? The website of Kubernetes explains what it is.
Minikube is a tool that makes it easy to run Kubernetes locally. Minikube runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a Virtual Machine (VM) on your laptop for users looking to try out Kubernetes or develop with it day-to-day.
-- Kubernetes https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/learning-environment/minikube/
Kubernetes vs Docker-compose vs Docker Swarm
Kubernetes is for running and connecting containers on multiple hosts (= cluster). Each node is a VM or a physical computer that serves as a worker machine in a Kubernetes cluster according to their explanation.
See the following stackoverflow for more detail:
What's the difference between docker compose and kubernetes? - stackoverflow
What's the difference between docker compose and kubernetes? - stackoverflow
For docker/docker-compose, see "how to use docker/docker-compose to create Laravel environment".
Use minikube
Install minikube
See this page of Kubernetes. This tutorial is well written.
Use minikube and kubectl
Simply run this command to start minikube.
$ minikube start
Then you will see these messages:
Now we are ready to use "kubectl" locally. Kubectl is a command line tool for controlling Kubernetes clusters.
Create nginx service
With
kubectl, we will use a container image nginx:1.7.9 to deploy nginx in our kubernetes cluster.
At first, make sure the maser node is working:
$ kubectl get all
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d7h
Then create yaml files somewhere as follows:
nginx_deploy.yml
nginx_deploy.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: nginx
replicas: 1 # tells deployment to run 1 pod matching the template
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.23.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
memory: 512Mi
cpu: "1"
requests:
memory: 256Mi
cpu: "0.2"
nginx_service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
name: nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
nodePort: 30080
name: http
selector:
name: nginx
externalIPs:
- 192.168.49.2
Save the files and run this command:
$ cd (the directory where you saved the two yaml files)
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx_deploy.yml -f ./nginx_service.yml
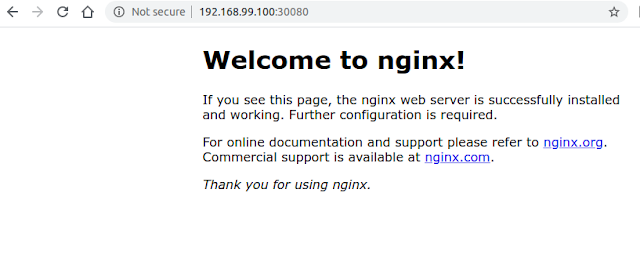
Check the nginx from browser
Check your minikube IP:
$ minikube ip
192.168.99.100
Check port number:
$ kubectl describe service/nginx
Name: nginx
Namespace: default
Labels: name=nginx
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"name":"nginx"},"name":"nginx","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"...
Selector: name=nginx
Type: NodePort
IP: 10.111.250.254
Port: http 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
NodePort: http 30080/TCP ####Port number is here!!!!!!!####
Endpoints: 172.17.0.4:80,172.17.0.5:80
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
Or simply use this command:
$ minikube service nginx --url
http://192.168.99.100:30080
Check from the browser with the IP and port. Confirm nginx is working in the cluster.
We can expose this nginx as loadbalancer:
$ kubectl expose deployment nginx-deployment --type=LoadBalancer --name=lb-nginx
$ minikube service nginx --url
http://192.168.49.2:30920
Then you can use this URL to access your service.
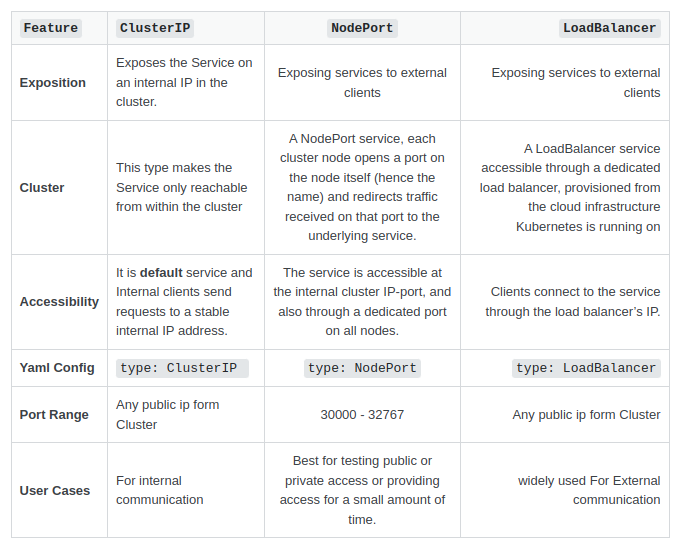
The difference between NodePort and LoadBalancer is:
image is from here: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41509439/whats-the-difference-between-clusterip-nodeport-and-loadbalancer-service-types
Create MariaDB service
Now we will create MariaDB service. At first, we will create the volume (space to save mariadb's data). Create the following files:
persistent_valume_claim.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
labels:
app: mariadb
name: mariadb-pv-claim
spec:
storageClassName: manual
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1000M
persistent_volume.yaml:
kind: PersistentVolume apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: mariadb-pv labels: type: local spec: storageClassName: manual capacity: storage: 1000M accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce hostPath: path: "/mnt/data"
Now apply the files:
$ cd (the directory where you saved the two yaml files)
$ kubectl apply -f ./persistent_volume.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f ./persistent_valume_claim.yaml The we will create deployment for mariadb. Create the following files:
mariadb_deploy.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mariadb-deployment spec: replicas: 1 # how many replicas of pods you want to create selector: matchLabels: app: mariadb template: # details for pods metadata: labels: app: mariadb # service will look for this label spec: # specification for Pods containers: - name: mariadb image: mariadb ports: - containerPort: 3306 env: - name: MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD value: secret resources: limits: memory: 512Mi cpu: "1" requests: memory: 256Mi cpu: "0.2"
and mariadb_service.yml:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mariadb labels: name: mariadb spec: selector: app: mariadb ports: - protocol: TCP port: 3306 targetPort: 3306
Save the files and run this command:
$ cd (the directory where you saved the two yaml files)
$ kubectl apply -f ./mariadb_deploy.yml -f ./mariadb_service.ymlNow you will have mariadb service:
$ kubectl get all
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 80m
lb-nginx LoadBalancer 10.103.22.52 <pending> 80:30150/TCP 27s
mariadb ClusterIP 10.103.28.199 <none> 3306/TCP 21m
nginx NodePort 10.109.85.209 192.168.49.2 80:30080/TCP 6sNow we will create configmap for mariadb service as "mariadb_configmap.yml":apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: mariadb-configmap
data:
database_url: mariadb
Then apply this file:$ kubectl apply -f ./mariadb_configmap.ymlNow we can use the mariadb:$ kubectl exec mariadb-deployment-644cf75948-9prh6 mariadb -- mariadb -uroot -proot -e "select version()"
version()
10.9.3-MariaDB-1:10.9.3+maria~ubu2204
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: mariadb-configmap data: database_url: mariadb
Then apply this file:
$ kubectl apply -f ./mariadb_configmap.ymlNow we can use the mariadb:
$ kubectl exec mariadb-deployment-644cf75948-9prh6 mariadb -- mariadb -uroot -proot -e "select version()"
version()
10.9.3-MariaDB-1:10.9.3+maria~ubu2204To access from outside of Pods, we need to expose the mariadb:$ kubectl expose deploy/mariadb-deployment --port 3306 --target-port 3306 --type LoadBalancer --name=mariadb-exposed
$ kubectl expose deploy/mariadb-deployment --port 3306 --target-port 3306 --type LoadBalancer --name=mariadb-exposedNow we can get the URL of the exposed mariadb:$ minikube service mariadb-exposed --url
http://192.168.49.2:31955
$ minikube service mariadb-exposed --url
http://192.168.49.2:31955
We can use this information to connect to the DB.
Cleaning up
To delete the service and deployment after confirming from the browser:
$ kubectl delete service/nginx service/mariadb deployment.apps/nginx-deployment deployment.apps/mariadb-deployment
$ kubectl delete pvc mariadb-pv-claim
$ kubectl delete pv mariadb-pv
$ kubectl get all